Custom Plastic Injection Molding Service With Short-Run Production
Medical Parts
Injection Moulding is highly repeatable; this means that all the
parts that are produced will be identical, which is especially
convenient for brand consistency and part reliability in high
volume production
Overview of Injection Molding:
Injection moulding enables complex shapes to be mass-produced with
a high level of efficiency and manageable costs. A wide selection
of materials allows engineers to exactly match the physical
properties they require for any given product. Additionally, the
application of multi-shot moulding techniques allows one to secure
an appealing visual appearance, as well as incorporating additional
functionality to the final product using materials that give high
mechanical properties. Yet, the actual process can be quite
multifarious, especially when it comes to achieving uniformity.
Injection Moulding Process:
Plastic injection moulding allows to produce large numbers of parts
with great accuracy and very quick cycle times from multi-cavity
tools. The general process of injection moulding involves a certain
amount of polymer materials being heated, melted, and injected into
a mould under high pressure. Further into the process, main
units of the injection moulding machine are:
a) feed hopper;
b) heated barrel;
c) crew (known as the injection unit);
d) clamp unit (which holds the mould together under the injection
pressures);
e) ejection unit (which removes the part from the mould).
Plastic Material Comparison Chart
Material | Approximate Tensile Strength | Impact Strength | Electrical Insulation | Temperature Resistance | Chemical Resistance | FDA Compliant | Cost (low to high) |
Acrylic (PMMA) | 8000 psi | low | no | high | strong | no | medium |
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | 5900 psi | high | no | low | medium | no | medium |
Nylon Polyamide (PA) | 12400 psi | high | yes | high | strong | yes | high |
Polycarbonate (PC) | 9500 psi | high | no | high | weak | yes (can contain bisphenol A, or BPA) | high |
Polyethylene (PE) | 1400 psi (LDPE)
3480 – 6530 psi (HDPE)
800 – 13100 psi (PET) | high (LDPE)
high (HDPE)
low (PET) | yes | low | strong (LDPE)
strong (HDPE)
strong (PET) | yes | low |
Polyoxymethylene (POM) | 6400 – 10600 psi | high | yes | high | strong | yes | high |
Polypropylene (PP) | 4800 psi | medium | yes | medium | strong | yes | low |
Polystyrene (PS) | 2560 – 7690 psi | high | no | | medium | yes | low |
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) | 290 – 8200 psi | high | no | low | strong | no | high |
The moulding process could be described by the following steps:
 Thermoplastic granules are prepared according to the manufacturer’s
guidelines. In some cases, this may mean that the material is dried
in a desiccant dryer to remove moisture — if the moisture isn’t
removed it could affect mechanical properties of the component.
Once prepared, the material is poured into the hopper of the
machine;
Thermoplastic granules are prepared according to the manufacturer’s
guidelines. In some cases, this may mean that the material is dried
in a desiccant dryer to remove moisture — if the moisture isn’t
removed it could affect mechanical properties of the component.
Once prepared, the material is poured into the hopper of the
machine;- The material enters the throat of the barrel via the hopper. The
plastic granules are collected by the helix of the rotating screw —
the feeding zone of the screw;
- The barrel is heated along its length using heater bands. There are
a number of zones depending on the machine size. The zones have
different temperatures along the length of the barrel. The
temperatures are set in conjunction with the material supplier’s
specification sheet;
- The screw rotates, which moves the material forward with the
pressure and determined rotational speed towards the compression
zone. This zone of the screw is designed to put a shear heat into
the plastic and to push the material against the barrel wall,
giving it a consistent melt. As the material is pushed through, it
enters the metering zone of the screw and fills the front of the
barrel;
- Once the material is injected via the nozzle at the end of the
barrel, it enters the runner system of the mould tool;
- The runner system allows the material to flow through a gate into
the cavity of the mould tool, which forms the shape of the finished
product;
- The mould tool is held at a constant temperature, which, again, is
defined by the material’s specification sheet. Keeping the tool at
a constant temperature allows heat to be drawn from the plastic
until it reaches its heat deflection temperature (HDT). The HDT is
also defined via the material’s specification sheet;
- Once the parts have reached the HDT, they will remain in a solid
state. The mould tool can be opened;
- Once ejected, the components fall into a boss. Parts also could be
collected from the mould via a robot or a conveyor belt;
- The tool closes and the whole process repeats.
The Many Benefits of Plastic Injection Molding:

l There are a host of benefits that come from producing parts through
plastic injection molding. They include:
l Infinite variety. Virtually any shape you can think of can be
manufactured as a plastic part.
l Intricate details. The force with which plastic is injected into a
mold ensures that even the tiniest spaces are properly filled.
l Low per-piece cost. While there are upfront costs for creating the
mold, highly automated production processes result in a very low
cost per part.
l High output. Parts can be produced very quickly.
l More cost-effective than machining. While the upfront cost of
machining may, in some cases, be lower, in the long run, plastic
injection molding is much more cost-effective.
l Resource-conscious process. The injection process uses only as much
material as needed for each part, and any material left at the end
of a process can be ground up and recycled.
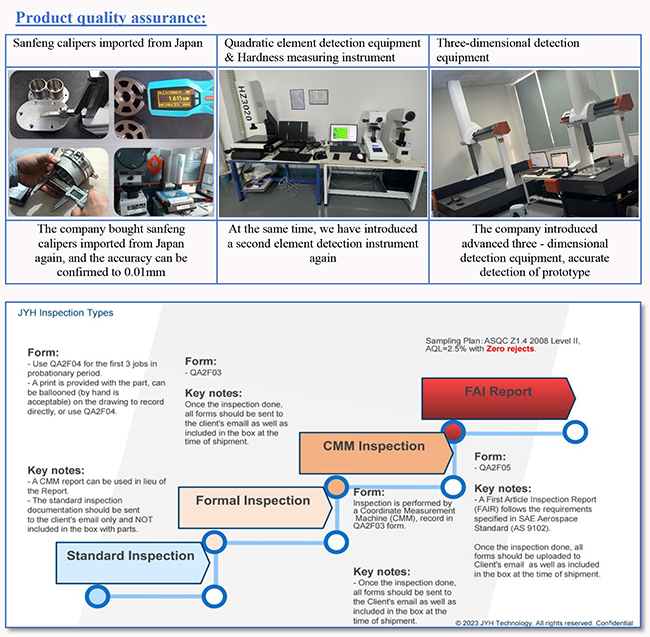
QC checking before ship the product:
Payment term:

Shipping way:

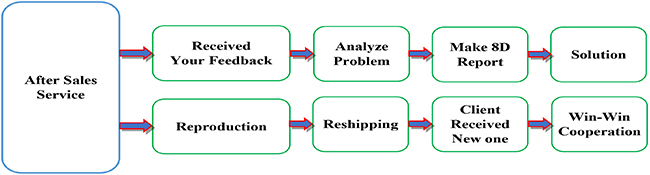
After service:
Custom Plastic Injection Molding Service With Short-Run Production
Medical Parts,JYH is your best injection mold supplier!
Injection Moulding is highly repeatable; this means that all the
parts that are produced will be identical, which is especially
convenient for brand consistency and part reliability in high
volume production.




 Thermoplastic granules are prepared according to the manufacturer’s
guidelines. In some cases, this may mean that the material is dried
in a desiccant dryer to remove moisture — if the moisture isn’t
removed it could affect mechanical properties of the component.
Once prepared, the material is poured into the hopper of the
machine;
Thermoplastic granules are prepared according to the manufacturer’s
guidelines. In some cases, this may mean that the material is dried
in a desiccant dryer to remove moisture — if the moisture isn’t
removed it could affect mechanical properties of the component.
Once prepared, the material is poured into the hopper of the
machine;








